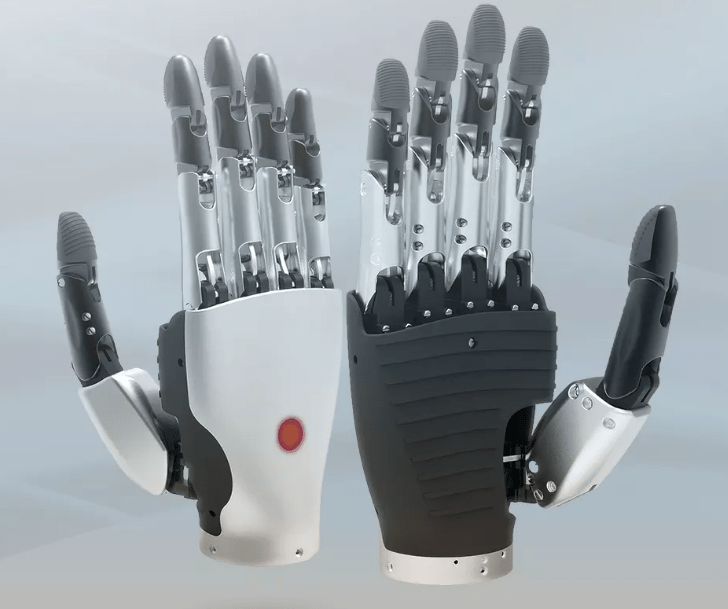
Concept
A robotic dexterous hand is a highly advanced end-effector designed to mimic the structure and functionality of the human hand. It integrates interdisciplinary technologies such as deep bionics, flexible sensing, micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS), and advanced materials. Unlike traditional robotic grippers optimized for specific tasks, dexterous hands prioritize versatility, enabling anthropomorphic operations like multi-finger coordination, adaptive grasping, and precise manipulation of objects.
Applications
Industrial Automation: Performs complex assembly, precision welding, and handling of fragile components in manufacturing.
Medical Rehabilitation: Assists in surgical procedures, prosthetics, and rehabilitation training with high-precision force feedback.
Aerospace: Executes maintenance and repair tasks in hazardous or microgravity environments.
Service and Humanoid Robotics: Enables human-like interactions, such as household chores, object manipulation, and collaborative tasks.
Key Parameters
Degrees of Freedom (DoF):
Ranges from 17 to 19 DoF per hand to replicate human-like movements (e.g., bending, twisting, and grasping).
Drive Systems:
Primarily electric motors for precise control, with alternatives including hydraulic, pneumatic, or shape-memory alloy actuators.
Sensing Capabilities:
Tactile sensors (1,000+ sensing points per hand) for texture, pressure, and slip detection.
Force/torque sensors and vision systems for real-time adaptive control.
Transmission Mechanisms:
Tendon-sheath systems for lightweight force transfer, complemented by linkage or gear mechanisms.
Material and Weight:
Lightweight alloys or composites (e.g., carbon fiber) to balance durability and agility.
Control Algorithms:
Machine learning and model predictive control (MPC) for autonomous task optimization and stability.
Evolution and Trends
Modern dexterous hands emphasize cost-effectiveness, modular design, and AI integration to expand their adoption in commercial and consumer robotics. Innovations focus on enhancing robustness, reducing complexity, and improving human-robot collaboration.

Share:
The Essential Guide to Robot Bearings: Types, Applications & Future Trends
SICUBE PHOTONICS: The Unrivaled Leader in DLP UV Projection for 3D Printing